At a depth of 100 meters underwater, an accident during a deep-diving mission not only revealed the extreme risks of cave diving but also highlighted the long-standing absence of underwater communication technology—a core pain point the industry can no longer ignore.

During that extreme dive, a diver failed to return as scheduled. The incident site, known as the "Mount Everest of China's underwater world," presented immense challenges for search and rescue due to its complex environment and staggering depth. This event serves as yet another grim warning: the absence of reliable underwater communication as a lifeline is an issue that can no longer be avoided.

Communication Principle: The Fundamental Logic of Underwater Communication—Why Rely on Sound Waves?
Although oceans cover 71% of the Earth's surface area, their unique physical environment renders them a communication blind spot. Once submerged, the traditional electromagnetic wave signals we rely on almost completely fail.
Electromagnetic waves face a near "death sentence" level of attenuation underwater. Seawater, in particular, contains a high concentration of inorganic salt ions, forming a highly conductive medium that rapidly absorbs and weakens electromagnetic energy. Neither the radio waves we use daily nor the far-infrared band lasers commonly employed in laser communication can escape this physical constraint.
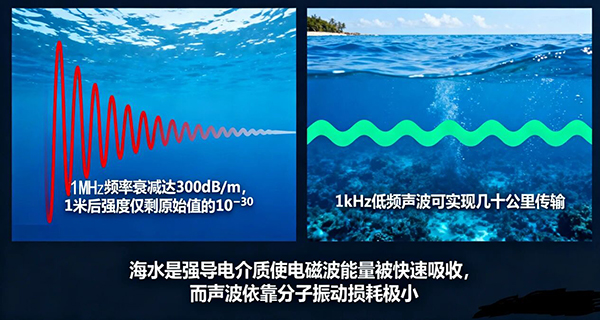
Research shows that electromagnetic waves at a frequency of 1MHz experience attenuation as high as 300 dB/m in water. This means that after traveling just one meter, the signal strength drops to 10^(-3) of its original value, completely losing its value for communication.
Therefore, whether mobile phone signals or satellite signals, none can effectively penetrate water—a fundamental limitation dictated by the inherent physical properties of electromagnetic waves.
In contrast, sound waves, leveraging their mechanical wave properties, become the "survival winner" for underwater communication. Sound waves transmit energy through the vibration of medium molecules, with an attenuation coefficient in water that is 3 to 5 orders of magnitude lower than that of electromagnetic waves. Low-frequency sound waves at 1 kHz can achieve long-distance transmission over tens of kilometers. Even 150 kHz ultrasonic waves experience far less attenuation compared to electromagnetic waves. Precisely for this reason, sound waves are currently the only feasible solution for underwater communication. However, it is important to note that the attenuation of high-frequency sound waves still increases rapidly with transmission distance.
The Power-Distance Scale: How Range Determines Technology Choice?
Underwater acoustic communication strictly follows the "power-distance" law: communication distance directly dictates the required transmission power and technical approach. This relationship can be expressed by the following fundamental formula:
Transmit Power (dBm) = Receiver Sensitivity (dBm) + Transmission Attenuation (dB) + Environmental Noise Margin (dB)
Taking consumer-grade acoustic receiving equipment as an example, its typical sensitivity is approximately -80 dBm (i.e., 0.1 nW), while environmental noise generally requires the system to reserve a margin of 10-20 dB. Among these, transmission attenuation is the most critical variable, increasing exponentially with communication distance.
The Power Black Hole: The Vast Gulf Between Theory and Reality
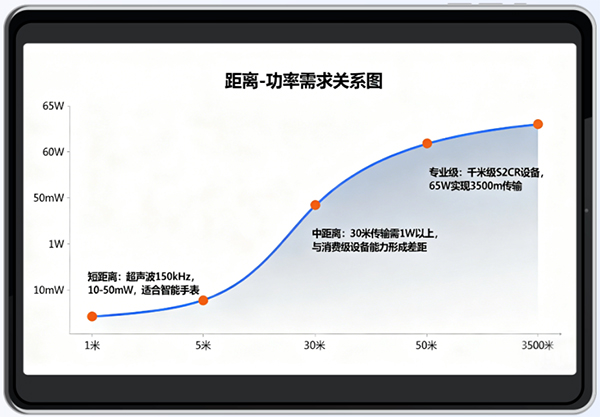
Technical solutions and power requirements differ significantly depending on the communication distance:
Short Distance (1-5 meters):
For example, data exchange between smartwatches requires about 10-50 mW of power, which remains within the tolerable range of such devices.
Medium Distance (5-50 meters):
Power requirements can skyrocket to over 1 Watt (W), far exceeding the power budget of ordinary consumer-grade devices.
Professional Grade (Kilometer-level):
Taking the S2CR series of professional equipment as an example, achieving 3500-meter transmission demands a transmission power as high as 65 W.
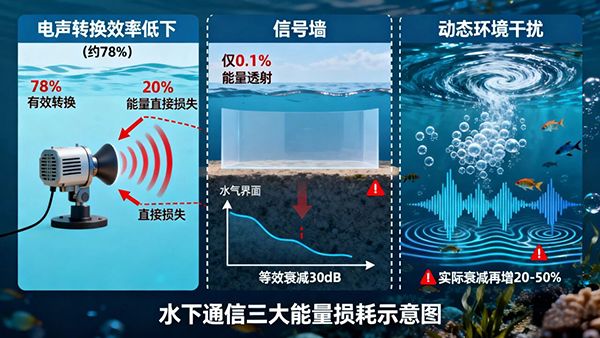
However, theoretical calculations often severely underestimate actual requirements, and a thousand-fold gulf may exist between theory and reality. This stems primarily from two major factors: first, efficiency losses during the electro-acoustic conversion process (approximately 22% of energy is lost in the acoustic-electric conversion); second, additional attenuation caused by dynamic environmental factors such as water quality, currents, and temperature variations, which can increase actual attenuation by 20% to 50% above theoretical values.
Thus, the ceiling for smartwatches is clearly defined:
Power Consumption Limit:
To ensure daily battery life, the average power consumption of its communication module must be strictly controlled at the milliwatt level.
Hardware Limit:
The maximum output power of the miniature piezoelectric ceramic transducer inside the watch is only 10-50 mW.
Thermal Dissipation Bottleneck:
Within the compact space of a watch-sized device, the heat generated by watt-level power transmission cannot be dissipated promptly, posing risks of device overheating and potential safety hazards.
Therefore, under the existing technological framework, the reliable underwater communication distance of smartwatches is strictly limited to within 10 meters.

Technical Breakthrough: Paths from Impossibility to Possibility
Facing the aforementioned stringent physical limitations, the industry is pursuing multi-path collaborative optimization to transform the concept of "watches transmitting rescue signals" into a highly practical solution.
Communication Goal Restructuring: Designed for Rescue
The core of rescue scenarios is not real-time voice communication but the transmission of minimal critical data. A 56-byte data packet containing location coordinates, status information, and a distress identifier is sufficient. Adopting a "burst mode" (single transmission ≤1 second) can keep average power consumption below 10 mW, thereby matching the battery life requirements of the watch.

Technical Optimization: A Two-Pronged Approach
Frequency Band Selection:
Using 18-34 kHz low-frequency sound waves reduces the attenuation rate by approximately 40% compared to the commonly used 150 kHz ultrasonic waves.
Energy Focusing:
Integrating digital beamforming technology to concentrate acoustic energy for directional transmission can improve effective gain by 5-10 dB.
Networking Rescue Mechanism: From Single Point to Network
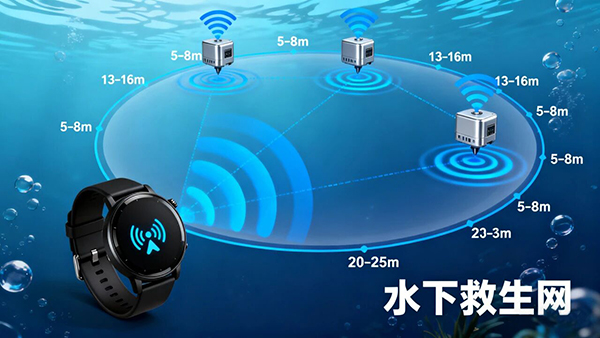
Setting the direct communication distance of a single watch at 5-8 meters. Once a distress signal is emitted, nearby diving companions wearing the same device can automatically become relay nodes to forward the signal. Through 3 levels of such forwarding, the effective rescue range can be extended to 20-25 meters, sufficient to cover most conventional diving scenarios.
Low-Power Design: Extreme Energy Efficiency
The device remains in sleep mode 99% of the time (power consumption ≤0.1 mW), waking periodically only to detect the environment. After triggering a distress signal, a "pulsed transmission" strategy is employed (transmitting once per second, 0.1 seconds per transmission), keeping average power consumption ≤5 mW. Simultaneously, through an advanced piezoelectric ceramic stacking structure, the acoustic energy conversion efficiency is increased to over 85% within the miniature volume.
Future Outlook: Breakthrough Directions from Theory to Reality
The fundamental path to achieving the next generation of breakthroughs lies in material innovation. Developing a new generation of piezoelectric transducers holds the potential to increase output power by 3-5 times within the same volume, laying the physical foundation for consumer-grade devices.
Simultaneously, algorithm optimization is also crucial. Using AI algorithms to adaptively adjust frequency and power in real-time based on environmental factors such as water quality and distance can dynamically match the optimal communication parameters, thereby maximizing the utilization efficiency of limited power.

The industry has already embarked on substantive exploration. For example, the "Dolphin Communication" system equipped in the Huawei WATCH Ultimate 2, based on micro-sonar technology, has enabled message transmission between watches within 30 meters and includes a built-in SOS distress function. This marks the first official step for consumer-grade devices into the field of underwater communication.
Conclusion
Every deep dive may face unknown risks. Establishing a reliable underwater communication lifeline is one of the most important safeguards that technological progress can offer explorers. As a veteran practitioner aptly stated, "We must prepare the best technology for the worst scenarios."
Today, the goal of technological innovation is clearly focused on this: enabling smart devices to become guardians of life even in extreme environments, providing more solid safety assurance for every descent. This is no longer merely a technological breakthrough but also the most steadfast response to the human spirit of exploration.













 Focus on us
Focus on us